Figur 17.169. Tillämpar exempel för filtret ”Gaussisk differens”

Ursprunglig bild

Filtret ”Gaussisk differens” tillämpat med radie 1 = 1,000 and radie 2 = 0,100.
Detta filter utför kantdetektering med den så kallade ”gaussisk differens”-algoritmen (Difference of Gaussians), vilken arbetar genom att utföra två olika gaussiska oskärpor på bilden, med olika oskärperadie för varje, och subtraherar dem för att få resultatet.
Denna algoritm används väldigt ofta i datorseende och är ganska snabb för att det finns väldigt effektiva metoder för att utföra gaussiska oskärpor.
- Förinställningar, ”Indatatyp”, Klippning, Toningsalternativ, Förhandsvisning, Sammanfoga filter, Dela vy
-
![[Notera]](images/note.png)
Notera Dessa alternativ beskrivs i Avsnitt 2, ”Gemensamma funktioner”.
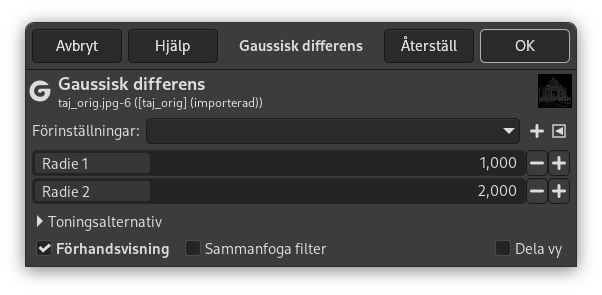
- Radie 1, Radie 2
-
Radius 1 and Radius 2 are the blurring radii for the two Gaussian blurs. Increasing ”Radius 1” tends to give thicker-appearing edges, and decreasing the ”Radius 2” tends to increase the ”threshold” for recognizing something as an edge.
If you want to produce something that looks like a sketch, in most cases setting ”Radius 2” smaller than ”Radius 1” will give better results.
I situationer där du har en ljus figur på mörk bakgrund kan att vända på dem till och med förbättra resultatet.