| Capítulo 8. Combinando imagens | ||
|---|---|---|

|
Parte II. Como posso me tornar um mestre no GIMP? |  |
Índice
You can think of layers as a stack of slides. Using layers, you can construct an image of several conceptual parts, each of which can be manipulated without affecting any other part of the image. Layers are stacked on top of each other. The bottom layer is the background of the image, and the components in the foreground of the image come above it.
There is no limit to the number of layers an image can have, only the amount of memory available on the system. It is not uncommon for advanced users to work with images containing dozens of layers. You can group layers to make your work easier, and there are many commands to handle layers.
The organization of layers in an image is shown in the Layers dialog, which is the second most important type of dialog window in GIMP, after the Main Toolbox. How it works is described in detail in the Layers Dialog section, but we will touch some aspects of it here, in relation to the layer properties that they display.
Each open image has at any time a single active drawable. A “drawable” is a GIMP concept that includes layers, but also several other items, such as channels, layer masks, and the selection mask. Basically, a “drawable” is anything that can be drawn on with painting tools. If a layer is currently active, it is shown highlighted in the Layers dialog, and its name is shown in the status area of the image window. If not, you can activate it by clicking on it. If none of the layers are highlighted, it means the active drawable is something else than a layer.
In the menu bar, you can find a menu called , containing a number of commands that affect the active layer of the image. The same menu can be accessed by right-clicking in the Layers dialog.
Cada camada em uma imagem tem alguns atributos importantes:
Every layer has a name. This is assigned automatically when the layer is created, but you can change it. You can change the name of a layer either by double-clicking on it in the Layers dialog, or by right-clicking there, and then selecting the top entry in the menu that appears, .
An alpha channel encodes information about how transparent a layer is at each pixel. It is visible in the Channel Dialog: white is complete opacity, black is complete transparency and gray levels are partial transparencies.
The background layer is special. If you have just created a new image, it only has one layer, which is the background layer. If the image has been created with an opaque Fill type, this one layer has no Alpha channel. To get a background layer with transparency, either create your new image with a transparent Fill type, or you use the Add an Alpha Channel command.
If you add a new layer, even with an opaque Fill type, an Alpha channel is automatically added to the layer.
Every layer other than the bottom layer of an image automatically has an Alpha channel, but you can't see a grayscale representation of the alpha values. See Alpha in Glossary for more information.
Figura 8.2. Exemplo de canal Alfa: Imagem básica
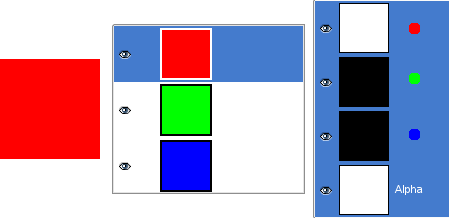
This image has three layers painted with pure 100% opaque Red, Green, and Blue. In the Channel Dialog, you can see that an alpha Channel has been added. It is white because the image is not transparent since there is at least one 100% opaque layer. The current layer is the red one: since it is painted with pure red, there is no green and no blue and the corresponding channels are black.
Figura 8.3. Exemplo de canal Alfa: Uma camada transparente
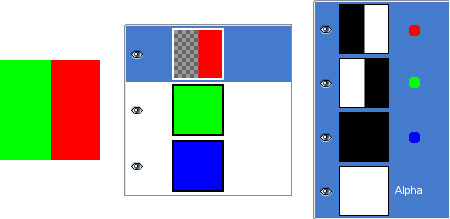
A parte esquerda da primeira camada foi deixada transparente (seleção retangular, Editar/Limpar). A segunda camada, verde, é visível. O canal alfa aparece ainda como branco, uma vez que existe uma camada opaca, nesta parte da imagem.
Figura 8.4. Exemplo de canal Alfa: Duas camadas transparentes
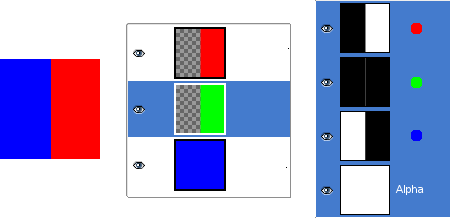
A parte esquerda da segunda camada foi tornada transparente. A terceira camada, azul, é visível através das primeira e segunda camadas. O canal alfa ainda é branco, uma vez que existe uma camada opaca, nesta parte da imagem.
Figura 8.5. Exemplo de canal Alfa: Três camadas transparentes
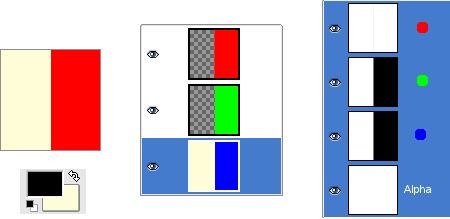
The left part of the third layer has been cleared. The Alpha channel is still white and the left part of the layer is opaque, because the background layer has no Alpha channel. In this case, the Clear command works like the Eraser and uses the Background color of Toolbox.
Figura 8.6. Exemplo de canal Alfa: Canal Alfa adicionado ao fundo
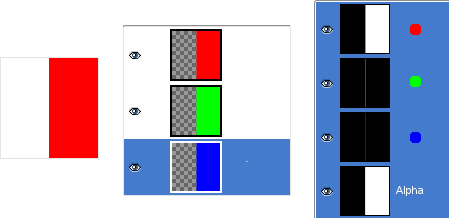
We used the → → command, on the Background layer. Now, the left part of the image is fully transparent and has the color of the page where the image is shown. The left part of the Alpha Channel thumbnail is black (transparent) in the Channel Dialog.
The layer type is determined by the image type (see previous section), and the presence or absence of an alpha channel. These are the possible layer types:
RGB
RGBA
Cinza
CinzaA
Indexado
IndexadoA
The main reason this matters is that some filters (in the menu) only accept a subset of layer types, and appear disabled in the menu if the active layer does not have a supported type. Often you can rectify this either by changing the mode of the image, or by adding or removing an alpha channel.
 Visibilidade
Visibilidade
É possível remover temporariamente uma camada de uma imagem, sem destruí-la, clicando sobre o ícone de “olho” na caixa de diálogo Camadas. Isso é chamado de “alternar a visibilidade” da camada. A maioria das operações de alteração de em uma imagem trata as camadas desligadas como se eles não existissem - exceto se ele for a camada ativa, mesmo desligada.Quando você trabalha com imagens que contêm muitas camadas, com diferentes opacidades, muitas vezes você pode obter uma imagem melhor do conteúdo da camada em que deseja trabalhar pela ocultação de algumas das outras camadas.
![[Dica]](images/tip.png)
|
Dica |
|---|---|
|
Se você clicar segurando Shift sobre o símbolo do olho, isso fará com que todas as outras camadas, exceto a que você clicar, fiquem ocultas. |
Usually, you activate a layer, to work on it, clicking it in the layer list. When you have a lot of layers, finding which layer an element of the image belongs to is not easy: then, press Alt and click with Mouse wheel on this element to activate its layer. The available layers will be looped through (starting from the upper one) while the Alt is held and the picked layer will be temporarily displayed in the status bar.
 Ligação para outras camadas
Ligação para outras camadas
Se você clicar entre o ícone do olho e a miniatura da camada, você terá um ícone de corrente, que permite agrupar as camadas para operações em várias camadas (por exemplo, com a ferramenta Mover ou uma ferramenta de transformação).
In GIMP, the boundaries of a layer do not necessarily match the boundaries of the image that contains it. When you create text, for example, each text item belongs to its own separate layer, and the layer size is automatically adjusted to contain the text and nothing more. Also, when you create a new layer using cut-and-paste, the new layer is sized just large enough to contain the pasted item. In the image window, the boundaries of the currently active layer are shown outlined with a black-and-yellow dashed line.
A principal razão pela qual isso é importante é que você não pode fazer nada em uma camada fora de seus limites: você não pode agir sobre o que não existe. Se isso causar-lhe problemas, você pode alterar as dimensões da camada usando qualquer um dos vários comandos que você pode encontrar na parte inferior do menu .
![[Nota]](images/note.png)
|
Nota |
|---|---|
|
A quantidade de memória que uma camada consome é determinada por suas dimensões, e não seu conteúdo. Então, se você estiver trabalhando com imagens grandes ou imagens que contêm muitas camadas, pode ter sentido deixar as camadas com o menor tamanho possível, embora em geral isso não faça diferença para o trabalho cotidiano. Se fizer, é melhor pensar em expandir a memória da sua máquina de trabalho. |
A opacidade de uma camada determina a medida que permite que as cores das camadas abaixo dela na pilha de camadas apareçam. A opacidade varia de 0 a 100, onde 0 significa transparência completa, e 100 significa opacidade completa.
O modo de uma camada determina como as cores da camada são combinadas com as cores das camadas abaixo para a produção de um resultado visível. Este é um conceito suficientemente complexo e importante, para merecer uma seção própria, que se segue. Veja Seção 2, “Modos de Camada”.
Além do canal alfa existe uma outra maneira de controlar a transparência de uma camada: adicionando uma máscara de camada, que é uma imagem em tons de cinza adicional associada à camada. Uma camada não tem uma máscara de camada de por padrão: ela deve ser especificamente adicionada. Máscaras de camada, e como trabalhar com elas, são descritas em mais detalhesna seção Máscara de Camada.