| 8.27. Descomponer | ||
|---|---|---|

|
8. El menú “Colores” |  |
Figura 16.203. Descomposición en imágenes (RGB)

Imagen original

Comando “Descomponer” aplicado (descomposición RGB), sin seleccionar la opción Descomponer en capas.
Figura 16.204. Descomponer en capas (RGB)

Imagen original
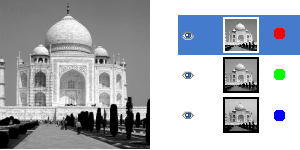
Comando “Descomponer” aplicado (descomposición RGB) con la opción Descomponer en capas seleccionada.
Este comando separa los canales (RGB, HSV, CMYK...) de una imagen en imágenes separas o en capas.
![[Nota]](images/note.png)
|
Nota |
|---|---|
|
This command only works on RGB images. If the image is Grayscale or Indexed, the menu entry is disabled. |
Extraer canales
Las opciones siguientes se describen con la opción Descomponer en capas marcada.
If the RGB option is chosen, a gray level image is created with three layers (Red, Green and Blue), and two channels (Gray and Alpha).
This function is interesting when using the Threshold tool. You can also perform operations like cutting, pasting or moving selections in a single RGB channel. You can use an extracted grayscale layer as a selection or mask by saving it in a channel (select the whole or a part of the layer, then → ).
If the RGBA option is chosen, an image is created similar to the RGB Decomposing with an additional Alpha layer filled with the transparency values of the source image. Fully transparent pixels are black and fully opaque pixels are white.
This option extracts the image transparency stored in the Alpha channel in the Channel dialog in a separate image. The fully transparent pixels are Black the fully opaque pixels are white. The graytones are smooth transitions of the transparency in the source image.
This option decomposes image into three grayscale layers, one for Hue, one for Saturation and another for Value.
Although Hue is grayscale, it does represent hues. In color circle, white and black are starting and arrival points and are superimposed. They represent Red color at top of circle. Gray intermediate levels are corresponding to intermediate hues on circle: dark gray to orange, mid gray to green and light gray to magenta.
Saturación y Valor: blanco es la máxima saturación (color puro) y el máximo valor (muy claro). Negro es la mínima saturación (blanco) y el mínimo valor (negro).
Esta opción es similar a HSV. En lugar del Valor, la tercera capa contiene el componente de la imagen L.
This option decomposes an image into four grayscale layers, one for Yellow, one for Magenta, one for Cyan, and one for Black.
This option can be useful to transfer an image into printing software with CMYK capabilities.
This option decomposes image into three grayscale layers, layer “L” for Luminance, layer “A” for colors between green and red, layer “B” for colors between blue and yellow.
La descomposición LAB es un modelo de color de la familia luminancia de color. Se usa un canal para la luminosidad mientras se usan otros dos para los colores. El modelo de color LAB lo usa Photoshop.
This option decomposes image into three grayscale layers, layer “L” for Luminance, layer “C” for Chroma, and layer “H” for Hue.
The LCH Decomposing is a color model of the Luminance-Color family.
In GIMP there are four YCbCr decompositions with different values. Each option decomposes an image in three grayscale layers, a layer for Luminance and the other two layers for blueness and redness.
The YCbCr color model, also called YUV, is now used for digital video (initially for PAL analog video). It's based on the idea that the human eye is most sensitive to luminosity, next to colors. The YCbCr Decomposing uses a transformation matrix and the different options are different values recommended by ITU (International Telecommunication Union) applied to the matrix.
If this option is checked, a new grayscale image is created, with each layer representing one of the channels of the selected mode. If this option is unchecked, every channel is represented in its own image and clearly named in the name bar.
Ejemplo 16.1. Marcas de recorte

Imagen original

Componente cian

Componente Negro
(Componentes magenta y amarillo omitidos.)
Esta opción es para especialistas. Está relacionada con la impresión CMYK. Cuando está marcada, cada píxel del color de primer plano activo será negro en cada componente de las imágenes o capas descompuestas. Esto permite hacer una marca visible de recorte en todos los canales, proporcionando una referencia útil para el alineado. Una cruz fina impresa en el registro de negro puede también verificar si las placas de impresión están alineadas.