Figure 17.81. Example for the Value Propagate filter

Original image

Filter “Value Propagate” applied
This filter works on color borders. It spreads pixels that differ in a specified way from their neighboring pixels.
- Presets, “Input Type”, Clipping, Blending Options, Preview, Merge filter, Split view
-
![[Note]](images/note.png)
Note These options are described in Section 2, “Common Features”.
- Mode
-
The examples will be about the following image:

- More white (larger value)
-
Pixels will be propagated from upper value pixels towards lower value pixels. So bright areas will enlarge.
Figure 17.83. More white

Bright pixels have been propagated to dark pixels in the four directions: top, bottom, right and left. Filter applied several times to increase effect.
- More black (smaller value)
-
Pixels will be propagated from lower value pixels towards upper value pixels. So dark areas will enlarge.
- Middle value to peaks
-
On a border between the selected thresholds, the average of both values is propagated.
Figure 17.86. Middle value to peaks

A thin border with a transitional color has been added to objects. It is not visible around objects with smoothed borders.

Green area zoomed x800. A thin border (one pixel wide) has been added. Its value is the average between gray (90%) and green (78%): (90 + 78) / 2 = 84.
- Color to peaks
-
The propagated areas will be filled with the foreground color of the toolbox.
A color selector opens, with a color picker.
Figure 17.87. Color to peaks
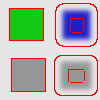
In this example, the selected color is Red. A thin border, one pixel wide, red, is added around objects. With smoothed objects, this border is located at the furthest limit of smoothing. Here, another border appears inside. This is an artifact due to the small size of the object which makes the smoothing area of opposite sides to overlap.
- Only color
-
Only areas with the selected color will propagate. With this option, soft and fuzzy edges don't propagate well.
Figure 17.88. Only color

In this example, the selected color is that of the green object. After applying filter several times, the green area is clearly enlarged.
- More opaque, More transparent
-
These commands work like “More white” and “More black”. Opaque (transparent) areas will be propagated over less opaque (transparent) areas. These commands need an image with an alpha channel.
Figure 17.89. More opaque

Original layer, with a transparent background.

Filter applied several times: the green, opaque, area got increased.
- Lower threshold, Upper threshold
-
A pixel will be propagated (spread) if the difference in value between the pixel and its neighbor is no smaller than the lower threshold and no larger than the upper threshold.
- Propagating rate
-
That's the propagating amount. The higher it will be the more colored the propagation will be.
- To top, To left, To right, To bottom
-
You can select one or more directions.
- Propagating value channel
-
If checked, the pixel's color channels (gray channel on grayscaled images) will be propagated. The option is checked by default, of course.
- Propagating alpha channel
-
If checked, the pixel alpha value will be propagated, otherwise the pixel will get the alpha of the neighboring pixels.