| 3. Brush Tools | ||
|---|---|---|
 |
Chapter 13. Toolbox |  |
The GIMP Toolbox includes thirteen “brush tools”, all grouped together at the bottom (in the default arrangement).
The feature they all have in common is that all of them are used by moving the pointer across the image display, creating brush-strokes. Four of them
the Pencil,
the Paintbrush,
the Airbrush and
the Ink tool
behave like the intuitive notion of "painting" with a brush. The others use a brush to modify an image in some way rather than paint on it:
the Bucket Fill fills with color or pattern;
the Gradient fills with gradients;
the Eraser erases;
the Clone tool copies from a pattern, or image;
the Perspective Clone tool copies into a changed perspective;
the Heal tool corrects small defects;
the Convolve tool blurs or sharpens;
the Smudge tool smears;
and the Dodge/Burn tool lightens or darkens.
The advantages of using GIMP with a tablet instead of a mouse probably show up more clearly for brush tools than anywhere else: the gain in fine control is invaluable. These tools also have special “Pressure sensitivity” options that are only usable with a tablet.
In addition to the more common “hands-on” method, it is possible to apply brush tools in an automated way, by creating a selection or path and then “stroking” it. You can choose to stroke with any of the brush tools, including nonstandard ones such as the Eraser, Smudge tool, etc., and any options you set for the tool will be applied. See the section on Stroking for more information.
Holding down the Ctrl key has a special effect on every brush tool . For the Pencil, Paintbrush, Airbrush, Ink Tool, Eraser, and Smudge tools, it switches them into “color picker” mode, so that clicking on an image pixel causes GIMP's foreground to be set to the active layer's color at that point (or, for the Eraser, GIMP's background color). For the Clone tool, the Ctrl key switches it into a mode where clicking sets the reference point for copying. For the Convolve tool, the Ctrl key switches between blur and sharpen modes; the the Dodge/Burn tool, it switches between dodging and burning.
Holding down the Shift key has the same effect on all brush tools: it places the tool into straight line mode. To create a straight line with any of the brush tools, first click on the starting point, then press the Shift key. As long as you hold it down, you will see a thin line connecting the previously clicked point with the current pointer location. If you click again, while continuing to hold down the Shift key, a straight line will be rendered. You can continue this process to create a series of connected line segments.
Holding down both keys puts the tool into constrained straight line mode. This is similar to the effect of the Shift key alone, except that the orientation of the line is constrained to the nearest multiple of 15 degrees. Use this if you want to create perfect horizontal, vertical, or diagonal lines.
Many tool options are shared by several brush tools: these are described here. Options that apply only to one specific tool, or to a small number of tools, are described in the sections devoted to those tools.
Paint Modes
The Mode drop-down list provides a selection of paint application modes. As with the opacity, the easiest way to understand what the Mode setting does is to imagine that the paint is actually applied to a layer above the layer you are working on, with the layer combination mode in the Layers dialog set to the selected mode. You can obtain a great variety of special effects in this way. The Mode option is only usable for tools that can be thought of as adding color to the image: the Pencil, Paintbrush, Airbrush, Ink, and Clone tools. For the other brush tools, the option appears for the sake of consistency but is always grayed out. A list of modes can be found in Section 2, “ Layer Modes ”.
In this list, some modes are particular:
Dissolve
Figure 13.34. Dissolve mode example
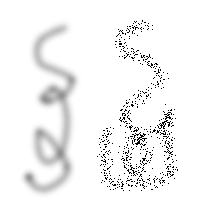
Two brush-strokes made with the Airbrush, using the same fuzzy circular brush. Left: Normal mode. Right: Dissolve mode.
For any paint tool with opacity less than 100%, this very useful mode doesn't draw transparency but determines the probability of applying paint. This gives nice patterns of dots to paint-strokes or filling.
Figure 13.35. Painting in Dissolve mode

This image has only the background layer and no Alpha channel. The background color is sky blue. Three strokes with Pencil and various opacities: 100%, 50%, 25%. Foreground color pixels are scattered along brushstroke.
Behind
This mode applies paint only to transparent areas of the layer: the lower the opacity, the more paint is applied. Thus, painting opaque areas has no effect; painting transparent areas has the same effect as normal mode. The result is always an increase in opacity. Of course none of this is meaningful for layers that lack an alpha channel.
In the above example image, Wilber is on the top layer, surrounded by transparency. The lower layer is solid light blue. The Bucket Fill tool was used, with the Fill Whole Selection option checked and the entire layer was selected. A pattern was used to paint with the Bucket Fill tool.
Figure 13.37. Painting in “Behind” mode
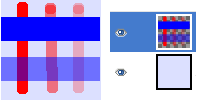
This image has two layers. The upper layer is active. Three brushtrokes with pencil, red color at 100%, 50%, 25% : only transparent or semi-transparent pixels of the layer are painted.
Color Erase
This mode erases the foreground color, replacing it with partial transparency. It acts like the Color to Alpha filter, applied to the area under the brushstroke. Note that this only works on layers that possess an alpha channel; otherwise, this mode is identical to Normal.
In the above example image, the color of the Bucket Fill tool was white, so white parts of Wilber were erased and the blue background shows through.
Figure 13.39. Painting in “Color Erase” mode
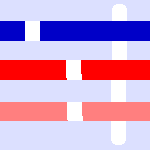
This image has only one layer, the background layer. Background color is sky blue. Three brushtrokes with pencil:
With the exact color of the blue area: only this blue color is erased.
With the exact color of the red area. Only this red color is erased, whatever its transparency. Erased areas are made transparent.
With the sky blue color of the layer background: only this color is erased.
The Opacity slider sets the transparency level for the brush operation. To understand how it works, imagine that instead of altering the active layer, the tool creates a transparent layer above the active layer and acts on that layer. Changing Opacity in the Tool Options has the same effect that changing opacity in the Layers dialog would have in the latter situation. It controls the “strength” of all brush tools, not just those that paint on the active layer. In the case of the Eraser, this can come across as a bit confusing: it works out that the higher the “opacity” is, the more transparency you get.
The brush determines how much of the image is affected by the tool, and how it is affected, when you trace out a brushstroke with the pointer. GIMP allows you to use several different types of brushes, which are described in the Brushes section. The same brush choices are available for all brush tools except the Ink tool, which uses a unique type of procedurally generated brush. The colors of a brush only come into play for tools where they are meaningful: the Pencil, Paintbrush, and Airbrush tools. For the other brush tools, only the intensity distribution of a brush is relevant.
This option lets you to modify precisely the size of the brush. You can use the arrow keys to vary by ±0.01 or the Page-Up and Page-Down keys to vary by ±0.05. You can obtain the same result if you have correctly set your mouse-wheel in the Preferences. See How to vary the height of a brush
The Pressure Sensitivity section is only meaningful if you are using a tablet: it allows you to decide which aspects of the tool's action should be affected by how hard you press the stylus against the tablet. The possibilities are opacity, hardness, rate, size, and color. They work together: you can enable as many of them as you like. For each tool, only the ones that are meaningful are listed. Here is what they do:
The effect of this option is described above.
This option applies to brushes with fuzzy edges. If it is enabled, the harder you press, the darker the fuzzy parts of the brush will appear.
This option applies to the Airbrush, Convolve tool, and Smudge tool, all of which have time-based effects. Pressing harder makes these tools act more rapidly.
This option applies to all of the pressure sensitive brush tools. If the option is checked, then pressing harder will increase the size of the area affected by the brush.
This option only applies to the painting tools: the Pencil, Paintbrush, and Airbrush; and only if you are using colors from a gradient. If these conditions are met, then pressing harder causes colors to be taken from higher in the gradient.
This option causes each stroke to fade out over the specified distance. It is easiest to visual for painting tools, but applies to all of the brush tools. It is equivalent to gradually reducing the opacity along the trajectory of the stroke. Note that, if you are using a tablet, this option does not change the effects of brush pressure.
You know “spacing” in brush strokes: strokes are made of successive brush marks which, when they are very near, seem to draw a continuous line. Here, instead of being aligned brush marks are scattered over a distance you can set with the slider.
The Incremental check-box activates incremental mode for the tool. If it is deactivated, the maximum effect of a single stroke is determined by the opacity, and moving the brush repeatedly over the same spot will not increase the effect beyond this limit. If Incremental is active, each additional pass with the brush will increase the effect, but the opacity can't exceed the opacity set for the tool. This option is available for all brush tools except those which have a “rate” control, which automatically implies an incremental effect. See also Section 2, “ Layer Modes ”.
Instead of using the foreground color (as shown in the Color Area of the Toolbox), by checking the "Use color from gradient" option you can choose to paint with a gradient, giving colors that change gradually along the brush trajectory. For basic information on gradients, see the Gradients section.
You have several options to control what gradient is used and how it is laid out:
Here you see a display of the current gradient. Clicking on it brings up a Gradient Selector, which will allow you to choose a different gradient.
Normally a brushstroke starts with colors from the left side of the gradient, and progresses rightward. If "Reverse" is checked, the stroke starts with colors from the right side, and progresses leftward.
This option sets the distance corresponding to one complete cycle through the gradient colors. The default units are pixels, but you can choose a different unit from the adjoining Units menu.
Figure 13.42. Illustration of the effects of the three gradient-repeat options, for the “Abstract 2” gradient.

Abstract2 Gradient

None

Sawtooth

Triangular
This option determines what happens if a brushstroke extends farther than the Length specified above. There are three possibilities: "None" means that the color from the end of the gradient will be used throughout the remainder of the stroke; "Sawtooth wave" means that the gradient will be restarted from the beginning, which will often produce a color discontinuity; "Triangular wave" means that the gradient will be traversed in reverse, afterwards bouncing back and forth until the end of the brushstroke.
Advanced users may be interested to know that brush tools actually operate at a sub-pixel level, in order to avoid producing jagged-looking results. One consequence of this is that even if you work with a hard-edged brush, such as one of the Circle brushes, pixels on the edge of the brushstroke will only be partially affected. If you need to have all-or-nothing effects (which may be necessary for getting a good selection, or for cutting and pasting, or for operating pixel-by-pixel at a high zoom level), use the Pencil tool, which makes all brushes perfectly hard and disables sub-pixel anti-aliasing.