| 7.54. Beskær lag | ||
|---|---|---|

|
7. Menuen “Lag” |  |
You can crop layer in two ways:
Crop to selection
Crop to content
The command crops only the active layer to the boundary of the selection by removing any strips at the edge whose contents are all completely unselected. Areas which are partially selected (for example, by feathering) are not cropped. If there is no selection for the image, the menu entry is insensitive and grayed out.
Figur 16.142. Applying “Crop to Selection”

On the left: before applying the command, the layer has a selection that has feathered edges.
On the right: after applying the command, the non-transparent pixels are not cropped, even if they are only semi-transparent.
The command automatically crops the active layer, unlike the Crop Tool, or the Crop to Selection command which let you manually define the area to be cropped.
This command removes the largest possible area around the outside edge which all has the same color. It does this by scanning the layer along a horizontal line and a vertical line and cropping the layer as soon as it encounters a different color, whatever its transparency.
You can use this command to crop the layer to the dimensions of a subject that is lost in a solid background which is too large.
Figur 16.143. “Crop to content” example

Before applying “Crop to content”
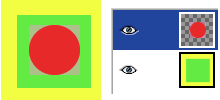
After applying “Crop to content”: the active layer, up, has been cropped to the size of the circle it contains. Its size is reduced, and the unoccupied part in the canvas is transparent, revealing the yellow and green colors of the underlying layer.