| 9.3. Distance Map | ||
|---|---|---|

|
9. Filters Algemeen |  |
Each pixel in the image is replaced with a gray value dependent on the distance to the nearest obstacle pixel, generally a boundary pixel. Different methods can be used to calculate the distance.
![[Opmerking]](images/note.png)
|
Opmerking |
|---|---|
|
Deze opties staan beschreven in Paragraaf 2, “Algemene Eigenschappen”. |
“Metric” is a topology term. Three methods are available:
Euclidean default: the distance is a straight line.
Manhattan: the distance is the sum of the one-dimensional distances along the X and Y axes.
Chebyshev: the distance is the maximum of the one-dimensional distances along the X and Y axes.
This defines how areas outside the input are considered when calculating distance. Choices are: Below threshold and Above threshold.
Default is 0. Increasing this value selects higher lightness pixels
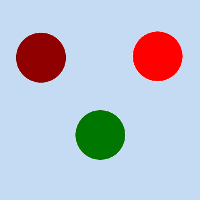
Original image for examples. Threshold low will be progressively increased. Lightness: dark red = 0.070; bright red = 0.223; green = 0.133
Afbeelding 17.182. “Threshold low” example

Threshold low = 0: only border distances are visible.

Threshold low = 0.070: “dark red” circle appears.

Threshold low = 0.133: “green” circle appears.

Threshold low = 0.223: “bright red” circle appears.
Default is 1. Decreasing this value makes result darker.
Number of computations for grayscale averaging.
This option is checked by default. If you uncheck it, no blur is created.